In accordance with the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), we are committed to safeguarding and ensuring your control over your personal data. By clicking “Accept All” you are permitting us to use cookies to enhance your browsing experience, assist us in analyzing website performance and usage, and deliver relevant marketing content. You can manage your cookie settings below. By clicking “Confirm” you are agreeing to the current settings.
AlSiC
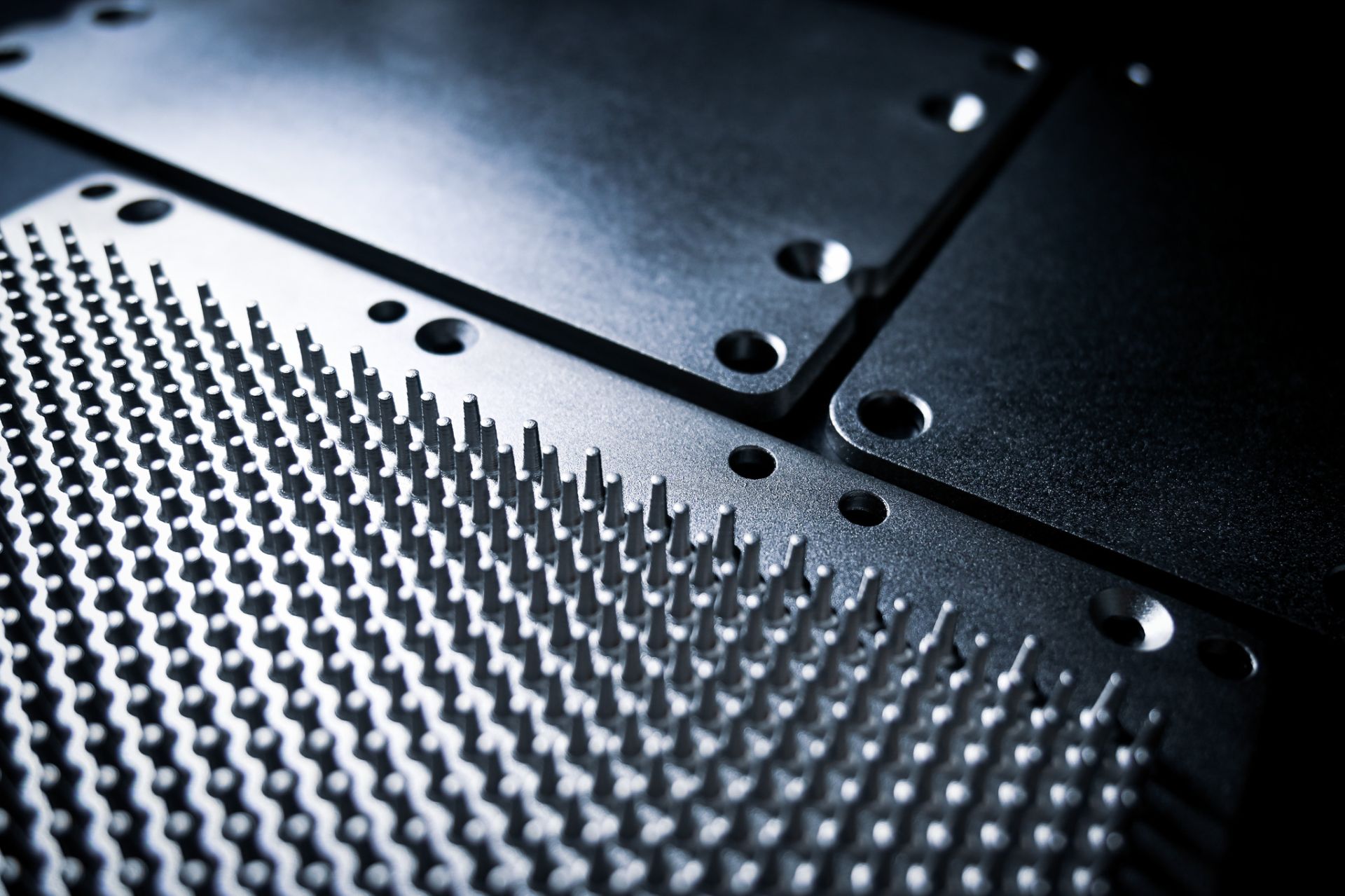
AlSiC Aluminum Silicon Carbide
- High thermal conductivity and high rigidity
- Coefficient of thermal expansion matched to semiconductor packages
- Excellent machinability
-
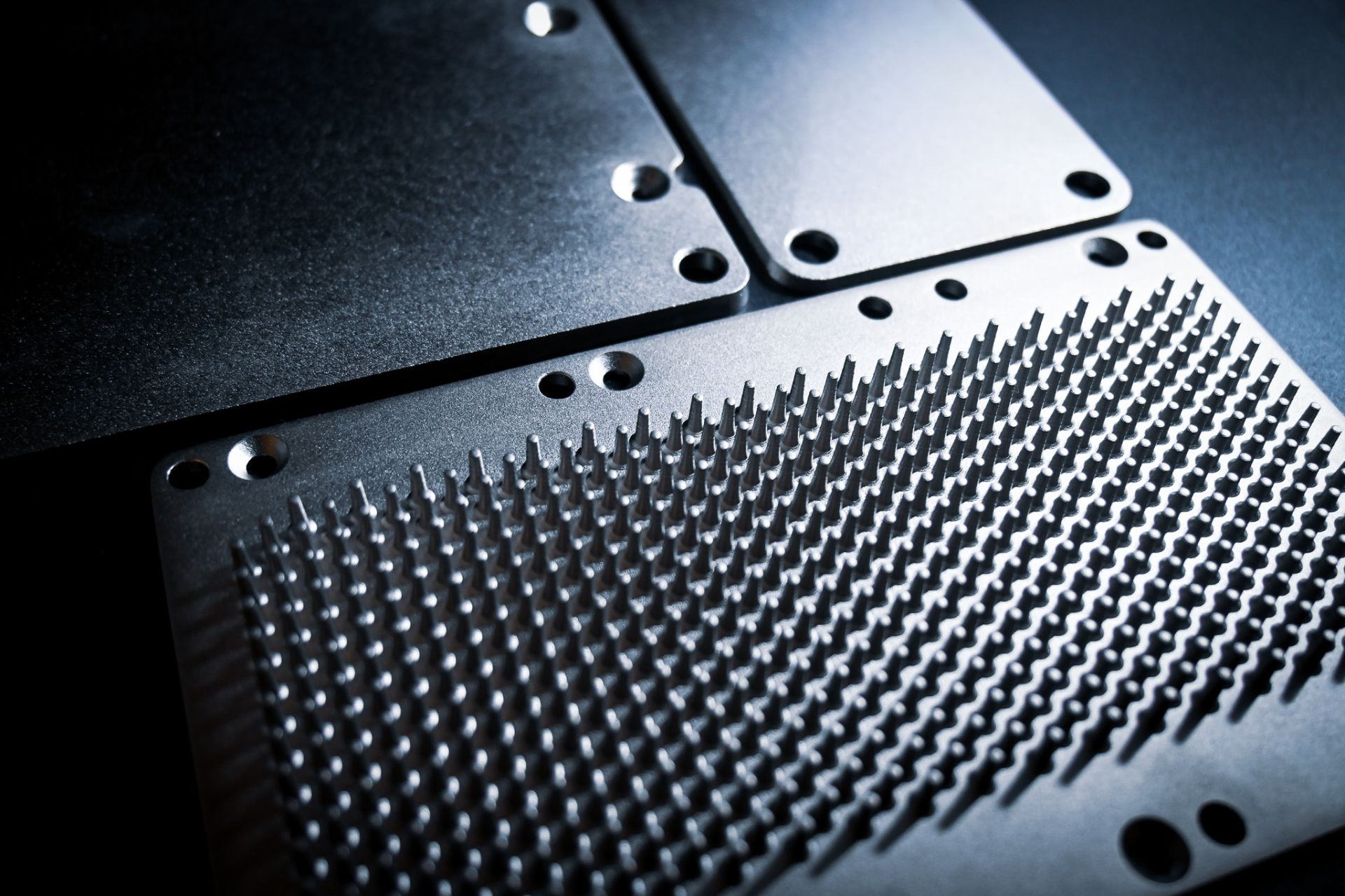
-
Key Application Advantages
AlSiC’s coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) can be engineered to match semiconductor chips and ceramic substrates, reducing thermal fatigue failure risks. Its high thermal conductivity ensures rapid heat spreading, improving overall system performance. Suitable for high-end IGBT modules, radar power modules, 5G base stations, and high-performance computing platforms.
AlSiC Thermal Structural Components
AlSiC thermal material can be formed and machined according to module design, offering lightweight, high strength, and thermal shock resistance. It is ideal for substrates, cover plates, housings, and other thermal management structural components. Its thermal conduction efficiency far exceeds that of conventional metals and effectively suppresses thermal deformation.
Thermal Conduction Comparison |
||
|---|---|---|
| Select the appropriate thermal structural component based on power density to optimize overall cooling performance | ||
| High Power Density Modules | Low to Medium Power Modules | |
AlSiC |
Vapor Chamber |
TIM |
| High-strength, high-thermal-conductivity composite material providing stable and reliable heat transfer and structural support. | Quickly spreads localized heat sources over a large area for improved cooling uniformity. | Reduces contact thermal resistance between the heat source and heatsink for enhanced thermal conductivity. |
 |
 |
 |


